Peptides are functional nutrients that are the most active, easily absorbed, and capable of stimulating the body’s regeneration system, positioned between large protein molecules and small amino acids. They are generally compounds formed by three or more amino acid molecules through dehydration condensation, with the amino acid molecules connected by amide bonds (—CONH—).
Peptides can be classified based on the number of amino acids they contain. For example, dipeptides, tripeptides, tetrapeptides, and so on, up to peptide chains composed of dozens or more amino acids, which are referred to as polypeptides or oligopeptides. Some literature also refers to peptides consisting of 2-10 amino acids as oligopeptides (small molecular peptides), while peptides composed of 10-50 amino acids (or sometimes 10-100 amino acids) are referred to as polypeptides, and those with more than 50 amino acids are classified as proteins.
Peptides and proteins participate in various physiological and biochemical processes, offering advantages such as good tolerance, high specificity, and minimal toxic side effects. This article continues from the previous discussion on the three most commonly used peptides in chemically synthesized cosmetic products and further introduces representative peptide components derived from animals and plants.
Copper Peptide
Blue copper peptide, also known as copper peptide, is a peptide formed by the combination of copper ions and amino acids, primarily found in marine organisms. Due to the presence of copper ions and a specific amino acid sequence in its molecular structure, it has unique properties and functions.
Dr. Loren Pickart isolated a tripeptide from human plasma, which spontaneously forms a complex when combined with divalent copper ions. This complex has proven effective in treating wounds and repairing skin damage, making it one of the longest-used and most representative reparative ingredients. Copper peptide helps in the production of collagen and glycosaminoglycans, accelerating cell proliferation to promote wound healing.
In cosmetics, copper peptide typically appears as blue copper peptide (scientific name: Tripeptide-1 Copper). Due to its excellent skin repair, anti-inflammatory, and moisturizing effects, it is widely used in the medical and aesthetic industries. For example, it can reduce scars in wound repair surgeries, promote healing after skin acne lesions, and repair damaged skin. Additionally, copper peptide has demonstrated certain antioxidant properties and anti-inflammatory effects, serving as an antioxidant and activator in tissue remodeling.
Brands like JM Solution and Cosmetic Skin Solution (a U.S.-based skincare brand) include copper peptides in their products, such as copper peptide serums. Currently, copper peptide is mainly used in skincare products as an antioxidant or moisturizer, and in medical aesthetics for scar repair. Its usage is not yet widespread, mainly due to its cost.
Copper Peptides at Creative Peptides
| CAT# | Product Name | M.W | Molecular Formula |
| CPC1613 | Copper Peptide(GHK-Cu) | 403.94 | C14H22CuN6O4 (Cu complex) |
| CPC1658 | Copper Peptide (GHK)2·Cu | 744.32 | C28H46CuN12O8 |
| CPC1708 | Prezatide Copper | 740.282 | C28H44CuN12O8 |
| R1966 | Prezatide Copper Acetate | 862.39 | C32H54CuN12O12 |
| HB00125 | Acetyl hexapeptide-3 | 888.99 | C34H60N14O12S |
Carnosine
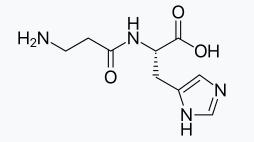
The scientific name of carnosine is β-alanylhistidine. It is a dipeptide composed of two amino acids: β-alanine and L-histidine, and it is a crystalline solid. Carnosine has strong antioxidant properties and can directly neutralize free radicals. The histidine residue in its side chain acts as a hydrogen donor, capturing free radicals and thus protecting cells from oxidative damage. This antioxidant ability makes carnosine particularly significant in anti-aging. (Note: Recent studies also suggest that carnosine’s antioxidant mechanism is related to the inhibition of telomere shortening.)
Additionally, when there is excessive sugar intake, excess glucose in the body can interact with proteins, amino acids, or lipids, leading to a process known as non-enzymatic glycation. This reaction results in the breakdown of collagen, leading to the loss of elasticity. Carnosine can act as a substitute, preventing glycation crosslinking of proteins, thereby helping to restore skin elasticity and brighten skin tone. Carnosine also helps maintain superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, neutralizing the large amounts of lactic acid produced by muscles, and serving to buffer the physiological pH.
Carnosine is considered one of the earliest bioactive peptides used in the beauty and skincare industry, with nearly a century of chemical synthesis history and a well-established manufacturing process. It, along with copper peptides and palmitoyl tripeptides, is one of the most widely used peptides in cosmetics and is active in many international skincare brands. For instance, L’Oréal’s La Roche-Posay includes carnosine in several product lines, such as the La Roche-Posay Effaclar Duo+ Acne Treatment. Olay also incorporates carnosine in products like the Olay Regenerist Micro-Sculpting Serum. Additionally, brands like Chando and Elizabeth Arden also include carnosine in their formulations.
Carnosines at Creative Peptides
| CAT# | Product Name | M.W | Molecular Formula |
| CPC1634 | Carnosine | 226.23 | C9H14N4O3 |
| 10-101-223 | N-Acetyl Carnosine | 268.27 | C11H16N4O4 |
| CPC1681 | Decarboxy Carnosine HCl | 255.14 | C8H16Cl2N4O |
| R1914 | L-Homocarnosine | 240.26 | C10H16N4O3 |
Glutathione
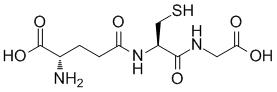
Glutathione is a tripeptide compound containing a γ-amide bond and a thiol group. It is composed of glutamic acid, cysteine, and glycine and is present in nearly every cell of the body. The thiol group (-SH) on the cysteine residue is its active group. Under physiological conditions, glutathione mainly exists in its reduced form (G-SH), but it can also exist in an oxidized form (G-S-S-G). The two forms can interconvert through the action of the enzyme glutathione reductase.
Recent studies have shown that glutathione can effectively reduce pigmentation by inhibiting the production of melanin, helping to prevent the formation of lipofuscin, or age spots. When used in combination with Vitamin C, it has been shown to have a good effect in treating melasma in women. Some experiments have also demonstrated that glutathione possesses certain tyrosinase inhibitory properties, making it a commonly used ingredient for whitening products.
Additionally, the thiol group (-SH) on the cysteine residue in glutathione exhibits strong nucleophilicity, allowing it to bind with heavy metal ions, drug metabolites, and other intermediates to form non-toxic or low-toxic complexes, which are then excreted from the body, playing a role in detoxification. Therefore, clinical treatments for melasma often combine glutathione with other agents such as the Jing Tian (Sedum) capsule for melasma removal, or with Vitamin C for treating dark spots.
Japanese brand Shiseido’s Anessa sunscreen is known for using a significant amount of glutathione. The famous French brand Filorga includes glutathione in its Brightening Collection, such as the Filorga Comfort Brightening Serum. In addition, brands like The Ordinary, Laneige, and Gu Yu also feature glutathione in their product formulations.
Frog Antimicrobial Peptide
Frog antimicrobial peptides are bioactive peptides extracted from the skin or secretions of amphibian species such as the Rana (tree frog). These peptides primarily come from the dorsal and ventral skin of the frog, serving as a defense mechanism developed through long-term natural selection. They typically consist of 10 to 50 amino acid residues and possess strong alkalinity, thermal stability, and broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties.
After the oil is extracted from the frog’s skin, it is rich in collagen and exhibits some degree of biocompatibility and degradability of functional proteins. It is considered a non-toxic active substance that, after self-assembly or cross-linking, can form collagen fibers with a certain strength and a degree of adhesion to wounds, offering a repair effect. The oil also contains a variety of amino acids and trace elements, including a high concentration of human chorionic gonadotropin, making it an ideal source of nutritional proteins. Theoretically, it also has antioxidant properties, and thus can be widely used in biotechnology and medical fields.
Compared to peptide-based substances, research and application of frog antimicrobial peptides are still in a relatively immature stage, with much of their potential yet to be developed. Current research focuses on enhancing the absorption and efficacy of frog antimicrobial peptides through biotechnology. For example, materials like chitosan are being used to prepare composite sponges that improve adhesion and water absorption, making them suitable raw materials for developing reparative skincare products.
Other peptides (Plant-Derived)
Soy protein-derived antioxidant peptides are a class of plant-derived peptides and an important branch of natural antioxidant peptides. These peptides are typically extracted from crops and vegetables through protein hydrolysis, and include varieties such as wheat bran peptides, mung bean peptides, soy peptides, and tea seed peptides. Among these, soy peptides have the longest history of development and use. They not only address issues like the poor solubility and instability of soybean proteins but also, through ultrafiltration enzymatic hydrolysis, produce peptide fragments with high antioxidant activity. These peptides are especially effective in inhibiting the formation of singlet nitrogen species.
The ability of soy peptides to scavenge hydroxyl radicals is closely related to the exposure of their amino acid side chains. Their antioxidant mechanisms are diverse and include, but are not limited to, directly capturing reactive oxygen species (ROS), activating the body’s antioxidant enzyme system, and chelating metal ions, thereby exerting a comprehensive antioxidant effect. These properties make soy protein-derived antioxidant peptides widely applicable in nutritional supplements, functional foods, and cosmetics.
Comparison of efficacy
| Type of Peptides | Functional Characteristics |
| Copper Peptide | Promotes the production of collagen and glycosaminoglycans, helping to enhance wound healing and skin tightening.Has antioxidant properties, reducing damage to the skin caused by free radicals.Possesses anti-inflammatory effects, aiding in skin inflammation repair.Helps improve signs of skin aging and enhances skin elasticity. |
| Carnosine | Possesses strong antioxidant capacity, clearing free radicals in the body and protecting cells from oxidative damage.Helps reduce melanin production, improving skin tone.Can reduce wrinkles and increase skin hydration.Contributes to maintaining immune system stability and cell viability.In athletics, enhances physical strength and endurance. |
| Glutathione | Acts as an internal antioxidant weapon of the body, providing widespread antioxidant effects and protecting cells from oxidative damage.Has detoxifying, whitening, and anti-aging physiological effects.Assists in removing toxic substances and repairing liver damage.Improves immunity and other functions.When used in skin care, helps whiten skin and improve uneven skin tone. |
| Frog Antimicrobial Peptide | Has immune-boosting properties, inhibiting the activity of viruses, bacteria, and tumors.Strengthens the body’s immune system, enhancing resistance.In clinical use, shows antiviral, anticancer, and liver-protecting effects. Examples include hepatitis treatment.As an immune factor, thymosin peptide is widely used in antiviral and health-support therapies. |